
Identifying natural hairline patterns and signs of balding is vital for proper hair maintenance and treatment. Widow’s peak and receding hairline often confuse people trying to determine their hairline patterns.
Though these patterns seem similar at first sight, they have unique causes and distinct features that impact future hair health.
This guide provides all the necessary information including features, key differences and best treatment options available for widow’s peak and receding hairline.
What Is A Widow’s Peak?
A widow’s peak appears as a V-shaped depression in the hairline at the center of the forehead. It gets its name from the peaked hoods worn by widows in the 16th century during their mourning period.
It exists due to natural genetic differences that control hair patterns during growth. These traits are inherited and run in families.
Experts suggest that widow’s peak may occur with autosomal dominant inheritance, which means children have a high probability of inheriting this trait from their parents.
Natural Widow’s Peak Features
Several distinct features will help you recognize a natural widow’s peak:
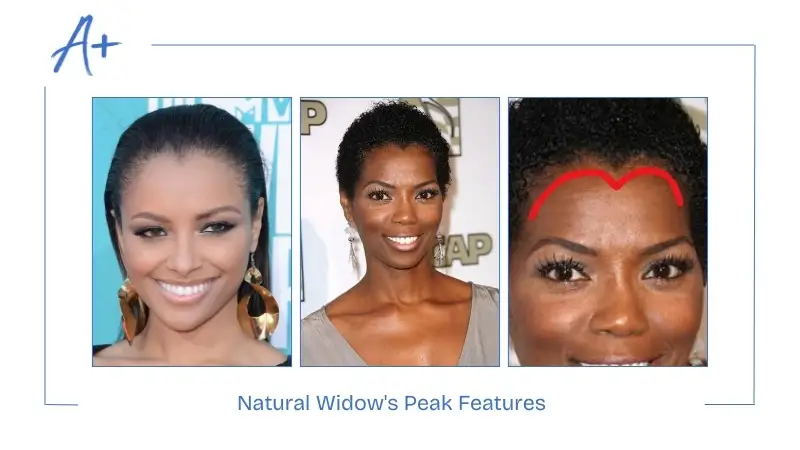
- Present From An Early Age: Widow’s peak is visible during early childhood or teenage years rather than showing up with a receding hairline.
- Consistent Shape: A V-shaped point shows consistent basic structure and placement from childhood until the end of life.
- Equal Distribution: The hair density adjacent to the widow’s peak shows identical patterns as the surrounding hairline.
- Family History: Individuals who have a distinctive hairline pattern often pass this characteristic through their family lineage.
- Gender-Neutral: Both men and women experience widow’s peak with equivalent prevalence.
What Is A Receding Hairline?
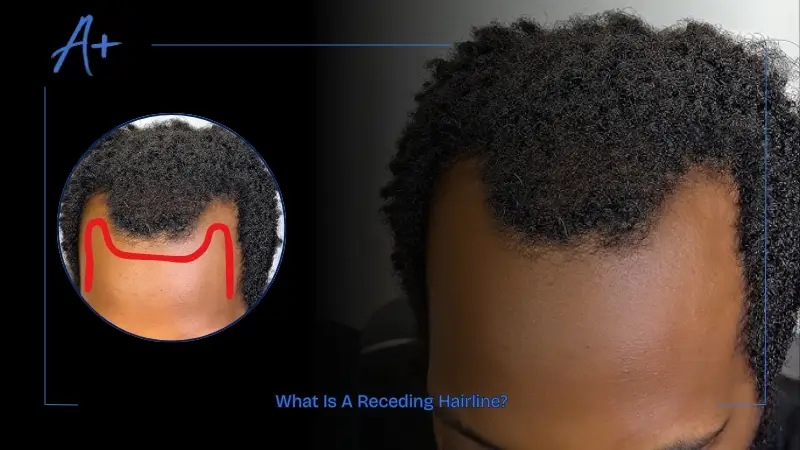
A receding hairline is distinct because it causes an ongoing backward movement of the hair from its natural frontal position, starting near the temples. This hair-loss pattern, known as androgenetic alopecia, affects both men and women.
The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), derived from testosterone, is the primary cause of hairline regression. Hair follicles in genetically vulnerable individuals react to DHT to create an ongoing miniaturization.
The normal hair growth cycles become progressively shorter, and hair strands become finer before follicles permanently cease producing hair.
Hair recession begins at the temples, leading to an M-shaped hairline, which can spread to cover the entire scalp. Men usually show more obvious signs of hair thinning, but women can experience different patterns that do not include frontal recession.
Receding Hairline Features
When observing a receding hairline, you will notice the following characteristics:

- Progressive Changes: Unlike the static features of a widow’s peak, the hairline moves backwards gradually over time.
- Temple Recession: The initial signs of hair loss appear as an M-shaped pattern that starts from the temples.
- Age Of Onset: Most cases appear during middle age, with people usually becoming aware of the condition between their late twenties and early thirties.
- Thinning Hair: Hair next to the hairline becomes thinner and more delicate.
- Family History Of Baldness: The condition tends to appear in people with a family history of male pattern baldness.
- Gender Distribution: More common in men with noticeable symptoms, but women can also develop milder symptoms.
Widow’s Peak vs. Receding Hairline – Detailed Comparison
Understanding the differences helps correctly diagnose and treat these hairline patterns. This table outlines essential characteristics for comparison:
| Feature | Widow’s Peak | Receding Hairline |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Genetic trait present from birth | Progressive hair loss condition |
| Shape | V-shaped point at center of forehead | M-shaped with temple recession |
| Age Of Onset | Present from childhood | Usually begins in adulthood |
| Progression | Stable, doesn’t change significantly | Gradually worsens over time |
| Hair Density | Normal hair density throughout | Gradually thinning hair |
| Gender Distribution | Equal in men and women | More common in men |
| Associated With Hair Loss | No | Yes |
| Treatment Needed | No (cosmetic only) | May benefit from treatment |
| Family Connection | Runs in families as a physical trait | Family history of pattern baldness |
| Hormonal Influence | Not hormone-dependent | Strongly influenced by DHT |
| Impact On Hair Health | No impact on hair follicle health | Progressive miniaturization of follicles |
| Future Hair Loss | No | Often indicates future pattern baldness |
Widow’s Peak vs. Receding Hairline – Practical Differences
Several practical steps can help you differentiate a natural widow’s peak from the early stages of a receding hairline.

1 – Photo Comparison
Compare current photos of your hairline with those from several years ago. A natural widow’s peak stays stable through time, but a receding hairline evolves significantly.
2 – Family History Assessment
Analyze hairline patterns among immediate family members of the same sex. Genetics determine V-shaped hairlines if widow’s peaks exist in your family without major baldness.
3 – Hair Density Evaluation
You need to thoroughly study the thickness of hair surrounding your hairline. Hair recession depends on how thin and delicate the hair near the temples is.
4 – Age Consideration
Your age and when you first noticed your hairline pattern are important. Widow’s peaks are present from childhood, whereas hair recession starts to appear in early adulthood.
5 – Pattern Observation
Check if the recession is symmetrical. The natural form of widow’s peaks is typically evenly shaped, even though early recession often appears uneven.
Widow’s Peak vs. Receding Hairline – Treatment Options
Here are some management tactics and treatments for widow’s peak and receding hairline:
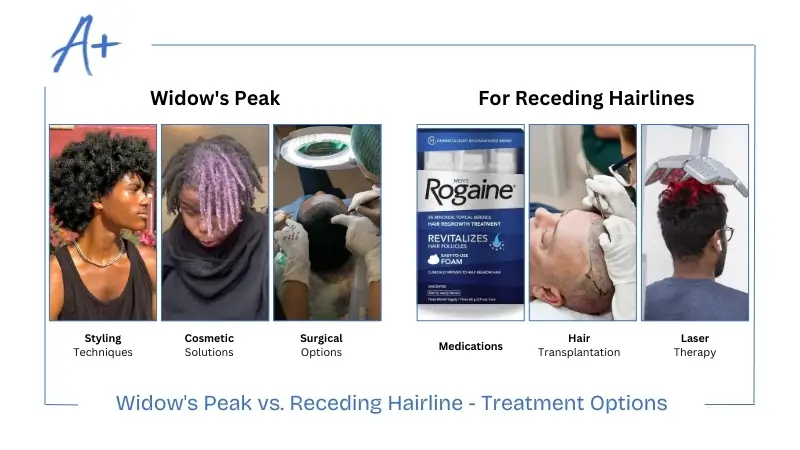
For Widow’s Peak
A widow’s peak being a natural inherited status requires no medical intervention since it does not qualify as a medical condition.
Personal alteration methods exist for people seeking changes in their appearance.
- Styling Techniques: Strategic styling can help hide a prominent widow’s peak. Voluminous hairstyles, bangs and textured hair can conceal the V-shaped point.
- Cosmetic Solutions: Temporary hair and powder solutions can create the appearance of a straighter hairline.
- Surgical Options: Hair transplantation exists for people who deeply care about their widow’s peak, but it should not be utilized when modifying natural attributes.
For Receding Hairlines
Several treatments are available for individuals affected by the actual hair recession.
- Medications: FDA approved treatments, including minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) can help stop and potentially reverse hair loss.
- Hair Transplantation: Modern hair restoration techniques like FUE and DHT offer patients the possibility to return lost hair to the affected areas through natural outcomes.
- Scalp Micropigmentation: This procedure creates an impression of short hair, which enhances the hairline appearance.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy can stimulate hair growth in some patients.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Reducing stress, proper nutrition and avoiding harsh hair treatments can improve your hair health.
When To Seek Professional Advice?
Consult a dermatologist or trichologist if changes to your hairline remain a concern. These professionals can:
- Distinguish between a natural widow’s peak and the initial signs of pattern baldness.
- Evaluate the speed and the style of hair loss.
- Advice about suitable treatments upon confirming hair loss.
- Identifying any medical factors causing hair loss.
- Individualized solutions that match your specific hair character and issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I have a widow’s peak or a receding hairline?
Check previous photos to identify a widow’s peak because the shape of your hairline through time reveals your condition. A hairline moving backward indicates recession.
Can a widow’s peak change into a receding hairline over time?
Genetic hair loss can cause a widow’s peak to reduce further.
What is the most attractive hairline?
Many found a gently rounded hairline most attractive for younger individuals.
What are the best treatments for an early receding hairline?
The FDA has approved minoxidil and finasteride as the most successful medical remedies.
How does a widow’s peak affect hair styling options?
Some dislike their widow’s peak because it makes styling the temple region challenging. Some choose flat hairlines and temples to maintain their hairstyle appearance.

